Volume 4, Issue 9
September 2024
Challenges and Solutions in Geriatric Care Management in Community Health Practices
Majed Saud Aloufi, Ahlam Hassan Alqarafi,Yazeed Saeed Alsenani, Wesam Nafea Alsharari, Khaled Saleh Alsharari, Khaled Dhaifallah Alharbi
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.52533/JOHS.2024.40904
Keywords: geriatric care, chronic diseases, frailty, long-term care, telehealth
Geriatric care management in community health practices faces significant challenges, including chronic diseases, frailty, polypharmacy, and deconditioning. These issues are intensified by the rapidly growing elderly population, especially in low- and middle-income countries. Telehealth, long-term care (LTC) services, and comprehensive geriatric assessments (CGA) have become crucial solutions. CGA provides a multidisciplinary evaluation that improves patient outcomes, while LTC services support older adults' functional abilities and dignity. Telehealth enhances access to care, reduces costs, and offers support to caregivers. Integrating these approaches, enhancing training for healthcare providers and developing supportive policies are crucial. This review underscores the need for a holistic, integrated strategy to address the complex needs of older adults, ensuring their well-being and optimizing healthcare systems. Future efforts should focus on standardizing CGA protocols, expanding LTC services within primary healthcare, promoting telehealth adoption and fostering research on effective interventions. These measures will ensure older adults receive comprehensive, effective and accessible care, improving their quality of life and reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
Introduction
Geriatrics, also known as geriatric medicine, is the medical specialty dedicated to the health of older adults. The term was created by Ignatz Leo Nascher, an Austrian American physician, in 1909, by merging the words ‘geri,’ meaning old, and ‘iatrics,’ the study of illness, to emphasize the differences between illnesses in older patients and normal aging (1).
Ageing populations are a global phenomenon; by 2050, there will be 1.6 billion older people, double the amount that existed in 2022 (771 million) (2). It is expected that the greatest shift would occur in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where 80% of all people over 60 will live by 2050 (3). Numerous societal changes, including those to healthcare systems, social assistance programmes, economic productivity, and family structures, are anticipated because of this demographic shift. There will be a comparable rise in demand for long-term care (LTC) services as the elderly population continues to expand. These solutions include therapy, rehabilitation, home and community-based care and healthcare monitoring. LTC services are intended to protect older people's inherent skills and functioning abilities, making sure that they are consistent with their fundamental freedoms, rights and humanity (4, 5). LTC services are becoming more important in helping older people as the healthcare system shifts from a disease-based strategy to a more comprehensive approach (3).
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has recognised the necessity of ensuring older people's access to LTC to promote health, prevent disease, preserve intrinsic capability and enable their functional ability considering this change (5). Three areas make up the public health framework for healthy ageing that the WHO has developed: the environment, long-term care and health services (6). These categories address a range of healthcare-related topics, including managing advanced chronic conditions, avoiding chronic conditions, assisting with early detection and control, reversing or moderating losses in capacity and encouraging behaviours that enhance capacity.
Research indicates that older adults' reduced functional ability is correlated with their increased use of healthcare services, which raises the expense of treatment and increases the risk of the establishment of institutions (3). Most LTC needs are still met mostly by family members or carers, even in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), despite mild improvements in the official delivery of LTC services. Therefore, it is imperative to incorporate LTC into the delivery of health systems to ensure that services are easily available to support and avoid functional decline in older adults (7).
WHO has created models and guiding principles to help with the smooth integration of LTC into health system policy, thereby enhancing accessibility and effectiveness in the provision of care (8). But establishing a successful LTC system is difficult and frequently requires commitments in a variety of care settings. The government struggles to integrate LTC into larger health system frameworks in many LMICs. They typically face resource constraints and competing objectives (9). Consequently, it is essential to identify, establish, and condense the worldwide LTC interventions and services for senior citizens, considering their impact on healthcare utilisation (3).
Review
In response to the growing elderly population, some medical schools and residency programs have increased trainees' exposure to geriatric care. However, advocacy is still needed to improve exposure at all levels of training and considerable variability remains in geriatric education programmes (10-13). Larger class sizes have made clinical experiences with specialized services less likely, given the small number of clinicians with the expertise to act as preceptors.
Chronic diseases
Geriatrics has traditionally been a specialty focused on managing chronic diseases, often alongside other conditions in older individuals, with regular monitoring to ensure patient stability. While these diseases cannot be cured, treatment aims to prevent progression and preserve quality of life and functional abilities. For stable patients, primary care is best positioned to monitor chronic diseases. Most chronic diseases progress slowly over the years, requiring some management adjustments. Primary care has the advantage of a long-term relationship with the patient, allowing for the recognition of minor deteriorations that might be missed by those who review patients irregularly (1).
Frailty
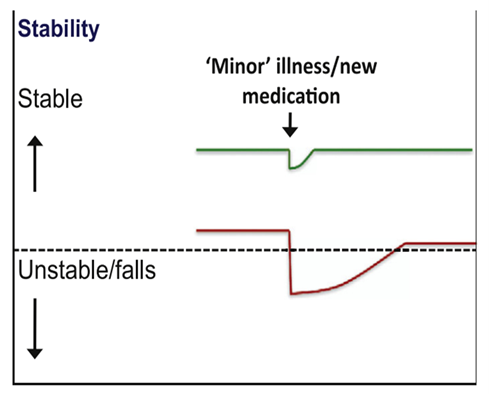
Frailty is a state of vulnerability that, although different from chronic disease and multimorbidity, often coexists with them. It is important to note that a person has frailty rather than is frail, to avoid the negative implications associated with the word frail. Vulnerability means that a minor stressor, such as a urinary tract infection or a move to a new location, can cause significant deterioration in the functional state of the patient, lasting longer than it would in a healthy individual. Since these older adults often live just above the independence line, such stressors frequently lead to new care needs or temporary placement in a 24-hour care facility. If not managed properly, the patient might be admitted to the hospital, facing all the risks associated with secondary care admission (Figure 1) (1).

Figure 1:Vulnerability of frail older adults to falls with a sudden change in health status after a minor illness. Used with permission by Dr A Clegg (1)
Frailty is not a static condition, and an individual can move between various stages. These stages have been categorized by various frailty identification tools. One commonly used tool is Rockwood’s Clinical Frailty Scale, which classifies functional ability on a scale of 1–7, from an elite athlete at 1 to severe frailty or complete dependence on others at 7 (Figure 2) (1, 14). Particularly important are those classified as vulnerable or mildly frail, corresponding to stages 4 and 5, respectively. Vulnerable adults are not yet dependent on others for activities of daily living (ADLs), while mildly frail individuals require help with higher-order ADLs. There is growing evidence that interventions at these stages can reverse or slow down the progression of frailty (15). Physical activity and resistance training show promising results, but more research is needed, particularly into physiological changes such as sarcopenia and immune aging.
Polypharmacy
Multiple conditions often necessitate multiple treatments. This phenomenon is termed polypharmacy and is particularly significant in older adults. Polypharmacy is often understood to mean writing a prescription for four to six different medications each day, while there is no agreed upon definition. Reasons for polypharmacy include multiple comorbidities and the single organ focus that has driven healthcare developments in recent years. Although medications are prescribed legitimately for specific conditions, the increased medication burden is not without danger, as it can lead to side effects, drug-drug interactions, and associated iatrogenic hospital admissions. It is also important not to be overly negative about medications, which should not be withheld on grounds of biological age alone. Withholding appropriate prescriptions can cause more harm than over-prescribing for an unwell patient and should be equally avoided. For example, an older diabetic patient may not need strict glycemic control but could be hospitalized with hyperglycemia and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state if not treated at all (1).

Figure 2: Clinical Frailty Scale (1)
Deconditioning
Deconditioning syndrome can be defined as a decline in physical, functional, and psychological abilities resulting from prolonged bed rest and inactivity. While usually seen in hospital inpatients, it is common among older adults in care homes and those living alone with care support. Deconditioning can affect anyone regardless of age, but in older adults, it starts earlier, is more common, more severe, and can often be irreversible. For many, this hospital-acquired functional decline can be so severe that it leads to premature institutionalization in a care home or even death (1).
The term deconditioning has been established through the first-ever national campaign to raise awareness about the harms of unnecessarily prolonged bed rest during hospitalization. The ‘Time to Move: Sit Up, Get Dressed, Keep Moving’ National Deconditioning Awareness and Prevention Campaign aimed at staff and the public (16), and the #EndPJparalysis campaign (2018) have been immensely successful in raising awareness and generating action to try to reverse the unintended harms a hospital admission can have on an older patient. These campaigns focus on reducing the burden of admission, but it is better to prevent deconditioning from occurring in the first place.
Management
Given their complexities, an important question arises: who should treat these patients? While single-organ specialists may be appropriate during acute phases, managing multiple comorbidities requires a more holistic, generalist approach. This challenge is compounded by a lack of evidence-based medicine for older adults. Clinical trials typically focus on single-organ diseases and often exclude older adults based on age and/or comorbidity (17), forcing clinicians to extrapolate from available clinical data or, in some cases, guess that the treatment will work. The second consideration is where these patients should be treated. The nature of chronic diseases implies a lack of cure and necessitates that patients adapt and live with their conditions. Therefore, the burden of treatment usually falls on primary care or community teams, with the goal of avoiding hospital admissions where possible. While community care might be the ideal solution, primary care cannot be expected to have the expertise to manage all chronic diseases in the elderly, and in some situations, hospital admission may still be the best option for the patient. Many patients are admitted to acute hospitals when their needs could have been met in the community if the right facilities were available. Conversely, many patients experience unnecessarily extended hospital stays due to a variety of reasons. This results in the harms associated with inappropriately prolonged hospitalization, leading to deconditioning and increased need for social care upon discharge (1).
Avoiding hospitals
Within the wider scope of chronic disease and frailty management, avoiding hospitals strategies play a crucial role. These strategies focus on older adults presenting to secondary care as emergencies who do not necessarily require admission. Many local areas in the United Kingdom have developed their own strategies, with the two most popular being community assessment teams and front-of-house teams based in Emergency Departments (18). Avoiding hospitals can be illustrated with the example of a fall. An older adult presenting with a fall and unable to mobilize will call emergency services. If not injured, a hospital avoidance community team, usually consisting of a paramedic or trained nurse and an occupational therapist, will assess the patient in their own environment. Quick interventions and suitable social arrangements can be promptly organized, allowing the patient to avoid setting foot in the hospital. However, if the patient suffers an injury, such as a distal radial fracture, they will still need to be assessed in the Emergency Department for an X-ray and cast. While the easy option might be to admit the patient due to the fracture and increased care needs, this poses risks of hospital-acquired infections and other harms associated with hospitalization, such as deconditioning. A timely intervention can prevent unnecessary admission, complete a comprehensive geriatric assessment, and allow for a safe discharge back to the community with appropriate social support. Appropriate patient selection is vital for hospital avoidance strategies to be effective, ensuring that patients are not denied secondary care treatment simply to keep them out of the hospital. When successful, these strategies provide patients with a comprehensive medical and social review without the need for hospitalization. Clear lines of corporate and clinical governance and accountability are essential when developing these services (1).
Telehealth
The term telehealth describes the practice of providing information and communication technology (ICT)-based remote healthcare services and information. It encompasses a broad range of services beyond traditional clinical interactions, including telemedicine, which focuses specifically on remote clinical services. Telehealth includes virtual consultations, remote monitoring, patient education and the management of chronic diseases, offering a flexible and accessible approach to healthcare. Telehealth offers numerous opportunities for the elderly to live and remain in their own homes as they age. The benefits and opportunities of leveraging telehealth for elderly care are explored and presented below from the perspectives of geriatric patients, caregivers and healthcare providers (19).
Geriatric patients
Recent technologies enable geriatric patients to maintain independent living and safely reside in their homes (20). Technology adoption bridges the generational technological gap by teaching elderly individuals how to use technology to assist with ADLs and strengthen communication with friends and family (21). Several studies have highlighted the positive impact of telehealth technology on elderly individuals, including empowerment, improved quality of life and care and better clinical outcomes (20, 22, 23).
Using telehealth helps reduce the cost of face-to-face visits to healthcare providers, hospital readmissions, emergency department visits, and travel expenses (24). Telehealth facilitates convenient access to services for patients with limited mobility, supporting self-management of chronic conditions. It reduces the need for long trips to attend follow-up visits, especially for those living in rural and remote areas. Additionally, telehealth can improve patient autonomy by helping them understand and control their well-being (25). Some authors suggest that telehealth provides better follow-up, enhances the doctor-patient relationship, improves healthcare services and encourages elderly patients to manage their chronic diseases (26). Several studies on the effectiveness of telehealth technologies for elderly patients show a reduction in mortality rates, hospital readmissions, length of hospital stays, and emergency department visits, as well as improved independence (27-29).
Caregivers
Caregivers, often family members or allied healthcare professionals, provide physical and emotional assistance to patients outside formal healthcare settings. They help the elderly perform ADLs and offer emotional and social support. Caring for patients with cognitive-related diseases, such as Alzheimer's and dementia, can be particularly challenging for caregivers (30). However, telehealth technologies enable caregivers to easily access social support networks and knowledge sources to better understand the disease, improve the patient-caregiver relationship, and reduce anxiety for both (19). Telehealth empowers caregivers to support and care for their elderly loved ones in the comfort of their own homes.
Healthcare providers
Telehealth functionalities allow healthcare providers direct access to elderly individuals across geographical distances and in remote locations. Telemonitoring enables healthcare providers to monitor patient health data in real time and analyse it. Providing necessary healthcare services remotely via telehealth minimizes travel and transportation-related expenses for healthcare professionals and improves their productivity. Regular contact with healthcare professionals accelerates diagnosis, prescription refills, minimizes emergency department visits, reduces acute hospitalizations, and improves the overall quality of life for patients (31). Telehealth also helps healthcare providers maintain connection with their patients and allows convenient access and direct communication with caregivers. The facilities provided by telehealth have opened new business opportunities in the healthcare industry by allowing professionals to expand their services to a wider population in various formats, whether as individuals, groups of professionals, or groups of healthcare institutions.
Mobile health applications
Mobile health applications are increasingly developed to help elderly patients manage their health and medications. These user-friendly apps offer features such as medication reminders, health monitoring, and patient education, which can significantly enhance medication adherence and overall health outcomes. By providing timely reminders and easy access to medical records, these apps empower older adults to take control of their health, reducing the risk of missed doses and improving chronic disease management. Additionally, apps tailored for the elderly can bridge technological gaps, promote independence, and facilitate communication with healthcare providers, thereby improving the quality of care and supporting healthy aging (32).
Conclusion
Effective geriatric care in community health practices requires integrated approaches, including CGA, LTC and telehealth, combined with enhanced training for providers and supportive policies. These strategies will improve the quality of life for older adults and optimize healthcare systems
Disclosures
Author Contributions
The author has reviewed the final version to be published and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Ethics Statement
Not applicable
Consent for publications
Not applicable
Data Availability
All data is provided within the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Funding
The author has declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work.
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable