Volume 4, Issue 7
July 2024
Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice toward the Use of Antibiotics without Prescription Among Citizens of Makkah City, Saudi Arabia
Raghad Majed Hariri, Khulood Waleed Melebari, Aljoharah Abdullah Alqahtani, Bushra Ahmed Shaikh, Rasha Ibrahim Kutbi, Deema Hani Beheiry, Mokhtar Mahfouz Shatla
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.52533/JOHS.2024.40702
Keywords: Antibiotics, Resistance, Saudi Arabia
Background: Misuse of antibiotics, including overuse, improper dosages, and insufficient treatment regimens, is a global health concern that exacerbates antibiotic resistance. The purpose of this study was to assess the knowledge, attitudes, and practices concerning the use of antibiotics without a prescription among residents of Makkah City, Saudi Arabia. Additionally, the study sought to identify the sources of antibiotics, reasons for their usage, and factors contributing to inappropriate patterns of antibiotic use within the community.
Methods: The current study adopts a survey based cross-sectional design. Data were collected via an online questionnaire distributed to the general population of Makkah City, Saudi Arabia. The inclusion criteria included the residents of Makkah City, aged 18 and above, and both genders.
Results: A total of 398 responses fulfilling the inclusion criteria were collected. The participants’ ages ranged from 18 to more than 50 years old, 60.8% of whom were females and 39.2% were males, with the majority of them (91.5%) being Saudi. The most reported reasons for antibiotic use were sore throat (74.9%), followed by fever (49%) and gastroenteritis (40.5%). Among the participants, the most commonly recognized adverse events associated with antibiotic use included antibiotic resistance (63.3%), allergy (46.5%), and rash (32.7%). The primary source of antibiotics for the majority of participants (78.6%) was a prescription from a physician, followed by previous personal experience (10.3%) and obtaining them from a pharmacist (6.3%). Approximately 56% of the participants reported having a full doctor’s appointment before using antibiotics, while 26.1% considered having adequate information about the drug, and symptoms that did not require a doctor’s consultation (16.8%) were deemed sufficient reasons to self-medicate using antibiotics. Overall, 72.1% of participants had a poor knowledge level regarding antibiotic use, while 33.6% of the younger participants had an overall good knowledge of the subject.
Conclusion: More than half of the population reported having poor knowledge levels regarding antibiotic use, while also stating that antibiotic resistance was their most known adverse event of antibiotic misuse.
Introduction
The issue of antibiotic resistance has become a significant global concern that negatively affects health; exposure to unnecessary or unsuitable antibiotics, together with incorrect dosages and treatment durations, raises the risk of developing antimicrobial resistance (1). Furthermore, incompletion of the medication course or missed doses might lead to inadequate treatment that fails to eliminate the bacteria, which facilitates the development of antibiotic resistance (2).
Around 3% of people in developed countries use antibiotics without a prescription, while this figure rises to nearly 100% in developing countries (3). Global research warns that without further intervention, antibiotic resistance could result in 10 million deaths annually by 2050, with economic losses reaching approximately 100 trillion USD (4). The prevalence of antibiotic resistance varies across different countries in the Middle East and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) region, with notable resistance observed among Gram-negative bacteria such as Acinetobacter, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. For instance, Saudi Arabia shows high resistance rates in Acinetobacter (83.3%) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (92.3%), while Klebsiella pneumoniae is notably resistant in Kuwait (36.2%) and Bahrain (13.9%). Gram-positive bacteria like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) are also prevalent, with significant resistance reported in Bahrain (76.5%) and Oman (58.3%) (5). Alarmingly, about one-third of all antibiotic prescriptions are unnecessary, exacerbating the issue (6). Certain bacteria are more prone to developing resistance due to high mutation rates and the selective pressure from widespread antibiotic use, posing significant dangers to public health through longer hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality (7).
In 2016, a cross-sectional study conducted among patients and their relatives visiting a hospital in Saudi Arabia found that education level, marital status, and the number of antibiotics used in the previous year all had a significant impact on awareness regarding antimicrobial use (8). Another study in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, demonstrated that adults in the general population lack awareness and comprehension of the population's safe use of antibiotics (9). Also in Taif, Saudi Arabia, a study showed that there were significant defects in the public's understanding of the use of antibiotics (10). Numerous international investigations have demonstrated that the public's ability to obtain antibiotics without a prescription is a major contributing factor to this issue (11, 12). Antibiotics are not dispensed without a prescription from doctors or other health professionals in developed nations (13), which is in contrast to self-medication, which is a practice commonly used in Saudi Arabia (14).
Given the absence of studies demonstrating the level of knowledge regarding antibiotic use among residents of Makkah City, this study aimed to investigate the status of knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding the use of antibiotics without a prescription in Makkah City, Saudi Arabia. Additionally, the study sought to identify the sources of antibiotics, reasons for their usage, and factors contributing to inappropriate usage patterns.
Methods
Study design and settings
The study presented is a survey based cross-sectional study. The data was obtained through an online questionnaire directed to the general population of Makkah City, Saudi Arabia.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The target population in our study comprised approximately 6 million residents of the Holy City of Makkah. Participants were invited to fill out the questionnaire via social media chats from March 15 to April 25, 2024. Inclusion criteria encompassed residents of Makkah city, aged 18 and above, of both genders. Exclusion criteria included individuals who were not residents of Makkah City. Participants under the age of 18 were excluded to target the adult demographic. Additionally, any incomplete questionnaires or responses were not considered. Healthcare professionals, such as doctors, nurses, and pharmacists, were excluded to avoid bias due to their advanced knowledge and different attitudes towards antibiotics.
Data collection
The online survey was designed to be easy and straightforward, using Google Forms. It was translated into Arabic and then sent to the targeted population through web links, along with details about the survey's objectives, the target population, and a voluntary participation request. The questionnaire utilized is similar to those used in two prior studies concerning the public use of antibiotics without prescription, one study targeted residents of Jeddah city (15), while the other focused on residents of Riyadh city (9). The questionnaire comprised several sections, including a consent form, sociodemographic data, and questions aimed at assessing participants' knowledge, attitudes, and practices concerning the use of antibiotics.
Sample size calculation
Raosoft was employed to determine the minimal sample size required for this study (16). Makkah has around 6 million residents, and we used a confidence interval of 95%. This suggests a sample size of about 385. To account for potential data loss, the total number of needed participants was calculated to be 400.
Ethical considerations
The study underwent submission to the Institutional Research Board of Umm Al-Qura University (UQU) to grant approval with IRB number HAPO-02-K-012-2024-02-2058, and no actions were initiated until this approval was obtained. No private or identifying information was gathered from any participants, ensuring privacy. Strict confidentiality measures were employed throughout data collection. Credit for the study was attributed to both the principal investigator and co-investigators. The participants’ confidentiality was guaranteed by securely storing the information using a system of codes, numbers, and pseudonyms. Access to the data was restricted to the researchers exclusively.
Statistical analysis
The data was collected, reviewed, and then imported to Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 26 (SPSS), released in 2019. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp. All statistical methods used were two-tailed with an alpha level of 0.05, considering significance if the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05. An overall knowledge score was computed by summing the correct answers, where the correct answer was given a 1-point score and 0 was given otherwise. Participants with knowledge scores less than 60% of the total correct answers were considered to have poor knowledge levels, while others with knowledge scores of 60–100% were considered to have good knowledge levels. Descriptive analysis for categorical data was done using frequencies and percentages, whereas numerical data was presented as the mean with a standard deviation. Also, participants' knowledge and awareness about antibiotic use, their attitude, and practice were tabulated, while the overall knowledge level was graphed. Cross tabulation was done to show the factors associated with participants' knowledge about antibiotic use and also to assess the relation between knowledge, practice, and attitude using the Pearson Chi-Square test and exact probability test for small frequency distributions.
Results
A total of 398 eligible participants completed the study questionnaire. The participants’ ages ranged from 18 to more than 50 years old, with a mean age of 29.5 ± 11.6 years old. A total of 242 (60.8%) were females, and the vast majority (91.5%; 364) were Saudi nationals. A total of 224 (56.3%) were single, and 164 (41.2%) were married. Considering educational level, most of the study respondents (87.2%; 347) were university graduates, while 239 (60.1%) worked in other fields than health care. Monthly income less than 5000 Saudi Riyal (SAR) was reported among 172 (43.2%), while 137 (34.4%) had monthly income exceeding 10,000 SAR. A total of 100 participants, representing 25.1% of the sample, reported possessing health insurance (Table 1).
|
Table 1. Socio-demographic characteristics of study participants, Makkah, Saudi Arabia |
||
|
Socio-demographics |
No |
% |
|
Age in years |
||
|
18-35 |
256 |
64.3% |
|
36-50 |
65 |
16.3% |
|
> 50 |
77 |
19.3% |
|
Gender |
||
|
Male |
156 |
39.2% |
|
Female |
242 |
60.8% |
|
Nationality |
||
|
Saudi |
364 |
91.5% |
|
Non-Saudi |
34 |
8.5% |
|
Marital status |
||
|
Single |
224 |
56.3% |
|
Married |
164 |
41.2% |
|
Divorced / widow |
10 |
2.5% |
|
Educational level |
||
|
Below university |
51 |
12.8% |
|
University |
347 |
87.2% |
|
Profession |
||
|
Non-health care field |
239 |
60.1% |
|
Health care field |
159 |
39.9% |
|
Monthly income |
||
|
< 5000 SR |
172 |
43.2% |
|
5000-10000 SR |
89 |
22.4% |
|
< 10000 SR |
137 |
34.4% |
|
Have health insurance |
||
|
Yes |
100 |
25.1% |
|
No |
298 |
74.9% |
In terms of participants' knowledge regarding antibiotic use (Table 2), the most commonly cited reasons for antibiotic usage were sore throat (74.9%), fever (49%), gastroenteritis (40.5%), cough (24.6%), and flu (18.3%). The most known adverse events among the study participants included antibiotic resistance (63.3%), allergy (46.5%), rash (32.7%), and difficulty breathing (24.9%), while 83 (20.9%) reported that antibiotics had no adverse events. A total of 214 (53.8%) reported that antibiotics were used for bacterial infections.
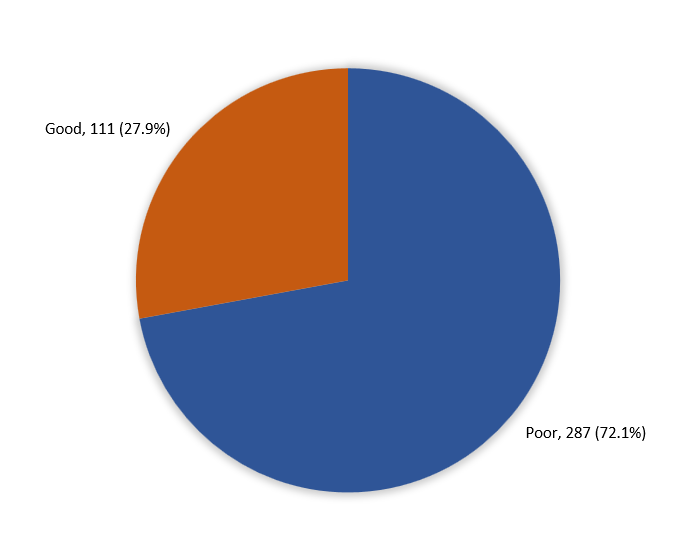
Overall, participants' knowledge regarding antibiotic use varied. Specifically, 111 individuals (27.9%) demonstrated a good level of knowledge, while the majority (72.1%; 287) exhibited a poor level of knowledge (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Overall Participants’ knowledge regarding the use of antibiotics, Makkah, Saudi Arabia
|
Table 2. Participants knowledge regarding the use of antibiotics, Makkah, Saudi Arabia |
||
|
Knowledge items |
No |
% |
|
Reasons for antibiotics use |
||
|
Sore throat |
298 |
74.9% |
|
Fever |
195 |
49.0% |
|
Gastroenteritis |
161 |
40.5% |
|
Cough |
98 |
24.6% |
|
Flu |
73 |
18.3% |
|
Adverse events of antibiotics |
||
|
Antibiotic resistance |
252 |
63.3% |
|
Allergy |
185 |
46.5% |
|
Rash |
130 |
32.7% |
|
Difficulty in breathing |
99 |
24.9% |
|
No side effects |
83 |
20.9% |
|
Type of infections for which antibiotics were effective |
||
|
Bacterial infections |
214 |
53.8% |
|
Viral infections |
16 |
4.0% |
|
Both of them |
80 |
20.1% |
|
I do not know |
88 |
22.1% |
Regarding participants' attitudes toward antibiotic use in Makkah, Saudi Arabia, the most commonly reported sources of antibiotics were prescriptions from physicians (78.6%), previous personal experience (10.3%), pharmacists (6.3%), advice from others (3.3%), and information from social media (1.5%). Considering reasons for self-medication, 223 (56%) reported full doctor's appointments, followed by having adequate information about the drug (26.1%), symptoms that did not require doctor consultation (16.8%), and lack of transportation (1%) (Table 3).
|
Table 3. Participants’ attitude regarding the use of antibiotics, Makkah, Saudi Arabia |
||
|
Attitude |
No |
% |
|
Source of antibiotics |
||
|
Prescription from the physician |
313 |
78.6% |
|
Previous experience |
41 |
10.3% |
|
Pharmacist |
25 |
6.3% |
|
Advice from others |
13 |
3.3% |
|
Internet and social media |
6 |
1.5% |
|
Reasons for self-medication |
||
|
Full doctor’s appointment |
223 |
56.0% |
|
Participant Adequate information about the drug |
104 |
26.1% |
|
Symptoms did not require doctor consultation |
67 |
16.8% |
|
Lack of transportation |
4 |
1.0% |
A total of 279 individuals (70.1%) reported discontinuing antibiotics at the end of the treatment course, 89 (22.4%) at the cessation of symptoms, and 30 (7.5%) upon completion of the prescribed medication. The prevalent antibiotics utilized were Augmentin (59.5%), Amoxil (40.2%), Zithromax (23.9%), and Fucidin (33.7%). Additionally, 93 individuals (23.4%) reported reusing leftover antibiotics, and 243 participants (61.1%) indicated that they read the product information before using antibiotics (Table 4).
|
Table 4. Participants practice regarding the use of antibiotics, Makkah, Saudi Arabia |
||
|
Practice |
No |
% |
|
When the antibiotics stopped |
||
|
At the end of the treatment course |
279 |
70.1% |
|
At the end of symptoms |
89 |
22.4% |
|
At the end of the drug |
30 |
7.5% |
|
Most common self-medicated antibiotics |
||
|
Augmentin |
237 |
59.5% |
|
Amoxil |
160 |
40.2% |
|
Zithromax |
95 |
23.9% |
|
Fucidin |
134 |
33.7% |
|
I don't know |
18 |
4.5% |
|
Reuse of leftover antibiotics |
||
|
Yes |
93 |
23.4% |
|
No |
305 |
76.6% |
|
Have read the product information before antibiotic use |
||
|
Yes |
243 |
61.1% |
|
No |
155 |
38.9% |
Factors associated with participants' knowledge about antibiotic use in Makkah, Saudi Arabia, revealed that 33.6% of young-aged participants exhibited overall good knowledge compared to 11.7% of old-aged participants, with a statistically significant difference noted (p = .001). Also, 32.1% of male participants had an overall good knowledge level in comparison to 25.2% of females (P =.048). A total of 41.5% of healthcare field employees had a good knowledge level compared to 18.8% of others (p =.001) (Table 5).
|
Table 5. Factors associated with participants knowledge about antibiotic use, Makkah, Saudi Arabia |
|||||
|
Factors |
Overall knowledge level |
p-value |
|||
|
Poor |
Good |
||||
|
No |
% |
No |
% |
||
|
Age in years |
.001* |
||||
|
18-35 |
170 |
66.4% |
86 |
33.6% |
|
|
36-50 |
49 |
75.4% |
16 |
24.6% |
|
|
> 50 |
68 |
88.3% |
9 |
11.7% |
|
|
Gender |
.048* |
||||
|
Male |
106 |
67.9% |
50 |
32.1% |
|
|
Female |
181 |
74.8% |
61 |
25.2% |
|
|
Nationality |
.164 |
||||
|
Saudi |
259 |
71.2% |
105 |
28.8% |
|
|
Non-Saudi |
28 |
82.4% |
6 |
17.6% |
|
|
Marital status |
.098 |
||||
|
Single |
152 |
67.9% |
72 |
32.1% |
|
|
Married |
127 |
77.4% |
37 |
22.6% |
|
|
Divorced / widow |
8 |
80.0% |
2 |
20.0% |
|
|
Educational level |
.281 |
||||
|
Below university |
40 |
78.4% |
11 |
21.6% |
|
|
University |
247 |
71.2% |
100 |
28.8% |
|
|
Profession |
.001* |
||||
|
Non-health care field |
194 |
81.2% |
45 |
18.8% |
|
|
Health care field |
93 |
58.5% |
66 |
41.5% |
|
|
Monthly income |
.105 |
||||
|
< 5000 SR |
121 |
70.3% |
51 |
29.7% |
|
|
5000-10000 SR |
72 |
80.9% |
17 |
19.1% |
|
|
< 10000 SR |
94 |
68.6% |
43 |
31.4% |
|
|
Have health insurance |
.587 |
||||
|
Yes |
70 |
70.0% |
30 |
30.0% |
|
|
No |
217 |
72.8% |
81 |
27.2% |
|
P: Pearson X2 test ^: Exact probability test * P < 0.05 (significant)
The relationship between participants' knowledge, practice, and attitude regarding antibiotic use in Makkah, Saudi Arabia, revealed that 82% of participants with good knowledge reported stopping antibiotics at the end of the treatment course, compared to 65.5% of those with poor knowledge, showing a statistically significant difference (p = .005) (Table 6).
|
Table 6. Relation between participants knowledge, practice and attitude about antibiotic use, Makkah, Saudi Arabia |
|||||
|
Attitude & practice |
Overall knowledge level |
p-value |
|||
|
Poor |
Good |
||||
|
No |
% |
No |
% |
||
|
Source of antibiotics |
.216^ |
||||
|
Prescription from the physician |
217 |
75.6% |
96 |
86.5% |
|
|
Pharmacist |
21 |
7.3% |
4 |
3.6% |
|
|
Previous experience |
33 |
11.5% |
8 |
7.2% |
|
|
Advice from others |
11 |
3.8% |
2 |
1.8% |
|
|
Internet and social media |
5 |
1.7% |
1 |
.9% |
|
|
Reasons for self-medication |
.620^ |
||||
|
Full doctor’s appointment |
162 |
56.4% |
61 |
55.0% |
|
|
Participant Adequate information about the drug |
73 |
25.4% |
31 |
27.9% |
|
|
Symptoms did not require doctor consultation |
48 |
16.7% |
19 |
17.1% |
|
|
Lack of transportation |
4 |
1.4% |
0 |
0.0% |
|
|
When the antibiotics stopped |
.005* |
||||
|
At the end of the treatment course |
188 |
65.5% |
91 |
82.0% |
|
|
At the end of symptoms |
73 |
25.4% |
16 |
14.4% |
|
|
At the end of the drug |
26 |
9.1% |
4 |
3.6% |
|
|
Have read the product information before antibiotic use |
.958 |
||||
|
Yes |
175 |
61.0% |
68 |
61.3% |
|
|
No |
112 |
39.0% |
43 |
38.7% |
|
P: Pearson X2 test ^: Exact probability test * P < 0.05 (significant)
Discussion
The present study aimed to assess the knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to non-prescription antibiotic use within the Makkah population. The study's results suggest a lack of adequate awareness regarding antibiotic usage, highlighting the need for educational interventions aimed at the public. Overuse of antibiotics can lead to consequential and severe adverse effects, such as the emergence and spread of antimicrobial-resistant strains. Previous studies have linked some factors contributing to the dissemination of antibiotic resistance within the community, such as incomplete adherence to treatment regimens, self-medication of antibiotics obtained without prescriptions, and unnecessary antibiotic use for conditions such as viral illness (11, 17, 18). These factors are further explored within the scope of this study.
In the current investigation, the majority of participants reported using antibiotics to address symptoms such as sore throat, fever, and gastroenteritis; similar results were reported in Jeddah, except that the respondents used antibiotics for flu more often than gastroenteritis (15). However, about 22.1% of the participants of the present study expressed uncertainty concerning antibiotic's effectiveness against bacterial versus viral infections; the same issue was elicited in research conducted in Jordan; this is in comparison to a study done in Sweden where the participants demonstrated a greater understanding in this regard (19, 20). Moreover, most respondents of the current study were aware of the adverse events of antibiotics, especially regarding antibiotic resistance (63.3%), compared with participants from Riyadh (9).
Among the participants, only 21.7% reported using antibiotics without a prescription, which contrasts significantly with the rate of 57.6% observed in a study conducted in Al-Kharj (21). In the present study, the primary reason for self-medication was having a complete doctor's appointment (56%), whereas respondents in Jeddah indicated that symptoms did not necessitate a doctor's consultation (37%) (15). However, a concerning observation from a study in Jordan, not investigated in the present study, was that 51.2% of physicians prescribed antibiotic for common colds, and 22.9% of physicians issued antibiotics prescriptions over the phone (19). Examining this antibiotic prescribing pattern among physicians in Makkah could be a focus of future research.
Augmentin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic containing amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, and it was observed to be the most common self-medicated antibiotic in this study (59.5%), followed by amoxicillin, which is sold under the brand name Amoxil (40.2%). Other studies observed the same preference for antibiotic usage, with Augmentin being the most common, followed by Amoxicillin (15), or Azithromycin (14). While most of the participants would stop the treatment at the end of the course (70.1%), similar studies revealed that the majority would stop the treatment after feeling better (9, 14). This variation could be attributed to a lack of patient education on the importance of finishing an antibiotic course even after the alleviation of symptoms.
It is observed through the data analysis of this study that the overall knowledge about antibiotic use is poor among the general population. Although participants within the age group 18-35 exhibited more awareness than the other age groups, it’s still minor compared with the higher percentage for poor knowledge in the same category. It is noticed that the different sociodemographic factors have no large effect on the knowledge and attitude toward antibiotic use, as even those who work in the healthcare field have a higher proportion of poor knowledge than good. Similar findings were concluded in other studies conducted throughout different cities in Saudi Arabia (10, 14, 17). Such findings prompt the need for more educational campaigns and reinforcement of better patient education regarding the correct use of antibiotics, the duration of their course, and the importance of adhering to them.
Limitations
This study was aimed at the citizens of Makkah City, Saudi Arabia. While the majority of the population is able to speak and read Arabic, the language in which the questionnaire was distributed, it is possible that those who can't were unable to participate. Also, being a single-centered study limits the generalizability of findings concerning Saudi Arabia. The cross-sectional nature can’t provide causality, therefore further multi-centered longitudinal studies are recommended.
Conclusion
It revealed that more than half of the targeted population will use antibiotics sourced from a physician’s prescription, with the most common reasons for antibiotic use reported being sore throat, fever, and gastroenteritis. The majority of the population stated antibiotic resistance as their most known adverse event of antibiotic use, followed by allergy and rash. More than half of the population was reported to have a poor knowledge level regarding antibiotic use, with the younger demographic having slightly better overall knowledge. We recommend increasing public awareness and education regarding the use of antibiotics, as it could have a positive impact on the population’s behavior and perception.
Disclosure
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding
None
Ethical Consideration
All the participants have been informed that no identifying information is needed, and consent was taken from them. Umm Al-Qura University Institutional Review Board issued the approval No. (HAPO-02-K-012-2024-02-2058).
Data Availability
All the data related to this study is available upon request.
Authors’ contributions
Raghad Hariri and Aljoharah Alqahani designed the study. Bushra Shaikh, Rasha Kutbi and Deema Beheiry conducted the literature search. Khulood Melebari and Aljoharah Alqahani acquired and analyzed data. Raghad Hariri proofread and revised the manuscript. Mokhtar Shatla supervised the research overall and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.